Clínica Boj » Caries treatment
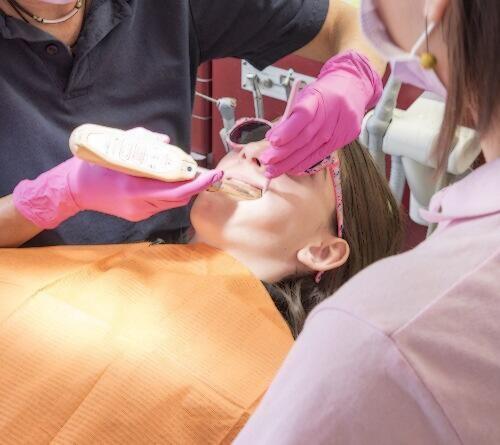
Paediatric and juvenile caries treatment
Presently paediatric and juvenile caries is the most frequent chronic disease among children, and has a high prevalence among the Spanish population.
In this multi-factorial disease, affecting in “milk teeth” as well as in permanent teeth, interaction with dependent factors of teeth, i.e. the type of diet, the bacterial plaque and time, are related.
What treatment should be performed in case of paediatric or juvenile caries?
Paediatric and juvenile caries should be treated differently depending on the location of the tooth decay, its progression and its activity.
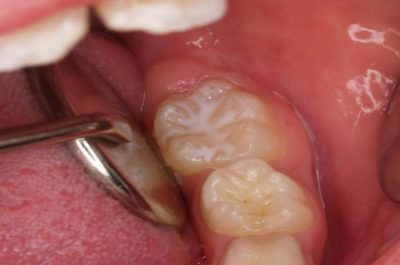
Early stages of child, teenager or young adult caries
We should always have a conservative approach in early stage of decay, using less invasive techniques such as pit and fissure sealants or other products that will allow us to remineralize the surface of the caries lesion.

Highly evolved caries in children, teenagers o young adults
In these cases, the paediatric or juvenile dentist will need to use esthetic composite materials to restore the tooth, and in cases where the dental nerve is also affected, he will need to perform a pulpal treatment. In some cases, it is also recommended the use of a crown (cover) when the amount of dental structure destroyed is too large due to the advanced state of the child´s, teenager´s or young adult´s caries.
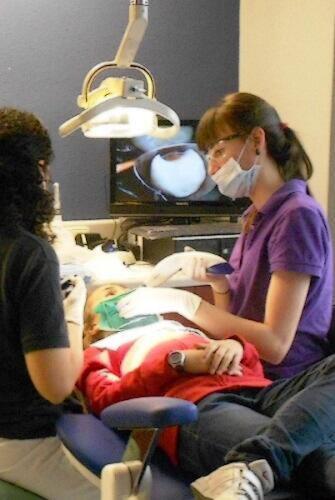
How does a paediatric or juvenile dentist treat caries?
The paediatric or juvenile dentist always tries to treat the tooth decay problem establishing an appropriate preventive and conservative approach adapted to the case. The correct dental hygiene habits, diets recommended by the paediatric or juvenile dentist, combined with a treatment that will restore the teeth, will allow avoiding future caries among the paediatric and juvenile population. This is the way to achieve an excellent oral health in children, teenagers and young adults. Paediatric and juvenile dentists always say: caries can always be prevented.
How long does it take for caries to destroy a tooth?
It will depend on every case. Active caries in paediatric or juvenile population with many risk factors will have a fast progression, while early stages of caries in highly motivated and involved in their own oral health children, teenagers or young adults, may progress slowly. The most important issue in these cases is early visits to the paediatric or juvenile dental clinic to find as soon as possible any type of problem.
What happens if caries is not treated?
The lack or postponement of tooth decay treatment may imply the appearance of pain, infection and inflammation of the tooth or the gum tissue in the child, teenager or young adult. We should bear in mind that a large caries lesion with huge tooth destruction may not be possible to treat and the tooth may need to be removed. In this case, the masticatory forces, the esthetics and the facial bones and muscular development will be affected, as well as the ability to keep the space between teeth in case of losing a temporary tooth.
How to keep teeth healthy?

Dental hypoplasia and hypomineralization
Dental hypoplasia is an illness that alters the quantity of enamel and mineral present in teeth, while dental hypomineralization is a quality problem of tooth enamel.
Pulpotomy and pulpectomy in children
Pulpotomy and pulpectomy are treatments performed on the nerve (pulp) of temporal teeth of children. In one case, the quantity of pulp tissue eliminated is partial and in the other total.
Paediatric and juvenile endodontics
Complete pulp tissue removal in permanent teeth of children, teenagers or young adults is called endodontics, and it normally takes place when a severe tooth decay exists.

Toothache
Children may have different type of toothaches or oral problems, since they are babies until they become young adults.


